杨辉三角
题目
给定一个非负整数 numRows,生成杨辉三角的前 numRows行。

在杨辉三角中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。
示例:
1 | 输入: 5 |
题解
- 动态规划
思路
如果能够知道一行杨辉三角,我们就可以根据每对相邻的值轻松地计算出它的下一行。
算法
虽然这一算法非常简单,但用于构造杨辉三角的迭代方法可以归类为动态规划,因为我们需要基于前一行来构造每一行。
首先,我们会生成整个 triangle 列表,三角形的每一行都以子列表的形式存储。然后,我们会检查行数为 0 的特殊情况,否则我们会返回 [1]。如果 numRows > 0,那么我们用 [1] 作为第一行来初始化 triangle with [1],并按如下方式继续填充:
1 | class Solution { |
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(numRows²)
虽然更新 triangle 中的每个值都是在常量时间内发生的,
但它会被执行 O(numRows²) 次。想要了解原因,就需要考虑总共有多少次循环迭代。很明显外层循环需要运行 numRows 次,但在外层循环的每次迭代中,内层循环要运行 rowNumrowNum 次。因此,triangle 发生的更新总数为1 + 2 + 3 + ... + *numRows*,根据高斯公式有
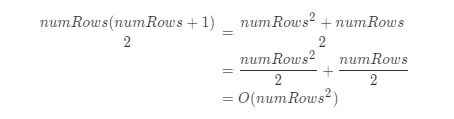
- 空间复杂度:O(numRows²)
因为我们需要存储我们在 triangle 中更新的每个数字,
所以空间需求与时间复杂度相同。
- Python解法
1 | class Solution: |
- 递归解法
通过numRows-1,求numRows行,递归求解
1 | class Solution { |